We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

FORMER BOP OFFICIALS SUPPORT COMPASSIONATE RELEASE CERTIORARI
 A month ago, I reported that the 6th Circuit ruled that USSG § 1B1.13(b)(6), the compassionate release guideline subsection that lets courts consider overly long sentences that could not be imposed under current law, exceeded the Sentencing Commission’s authority. Several other circuits have held the same, notably the 3rd Circuit in United States v. Rutherford.
A month ago, I reported that the 6th Circuit ruled that USSG § 1B1.13(b)(6), the compassionate release guideline subsection that lets courts consider overly long sentences that could not be imposed under current law, exceeded the Sentencing Commission’s authority. Several other circuits have held the same, notably the 3rd Circuit in United States v. Rutherford.
Rutherford is now before the Supreme Court on a petition for certiorari. The Justices have already relisted the case for more consideration (usually an indication that it is getting a serious look) at tomorrow’s conference.
Evidence of the Court’s interest came in Tuesday’s announcement that the Court would review a related issue, Fernandez v. United States. The issue in that case is whether whether a combination of “extraordinary and compelling reasons” supporting a sentence reduction under 18 USC § 3582(c)(1)(A) can include reasons that may also grounds for setting aside a sentence under 28 USC § 2255, the federal habeas corpus statute that can be used to attack the constitutionality of a conviction or sentence.

In Fernandez, a district court granted the prisoner a “compassionate release” for reasons that included the court’s belief that there was substantial evidence that he was actually innocent of the murder and that his sentence was disparately long compared to those of his co-defendants (who became informants). The 2nd Circuit reversed (and ordered Joe back to prison), holding that factors that would work for a § 2255 motion could not be relied on for § 3582(c)(1)(A) compassionate release.
The Circuit’s holding was contrary to decisions of the First and Ninth Circuits, which have each held that district courts are not restricted from considering matters under 18 USC § 3582(c)(1)(A) other than the sole restriction – rehabilitation alone cannot support compasionate release – set forth in the law by Congress. The Supreme Court will decide what limits, if any, cabin a judge on what he or she may consider as extraordinary and compassionate reasons for compassionate release.
Fernandez is Rutherford’s spiritual cousin. I would not be surprised to see certiorari granted to Rutherford, and the two cases being combined for argument and decision.
Rutherford is notable for something else: Supporting petitioner Rutherford are amicus briefs, including ones filed by FAMM, six clinical law school professors, and 12 former federal judges. Most interesting may be an amicus brief by former Bureau of Prisons officials (now corrections consultants) represented by civil rights attorney Scott Lewis at Boston firm Anderson & Krieger.
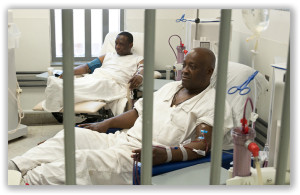 Spotlighting the BOP healthcare crisis, the brief argues that expanding access to compassionate release for inmates serving unusually long sentences would benefit the BOP because “aging, unhealthy inmates consume a disproportionate share of BOP’s scarce resources, which has cascading effects on federal prison operations and the safety and security of BOP staff, as well as inmates… [a]nd the thousands of prisoners potentially eligible for compassionate release who are serving ‘unusually long sentence[s]’ with ‘gross disparity…’ are especially likely to become elderly and unhealthy or disabled in prison.”
Spotlighting the BOP healthcare crisis, the brief argues that expanding access to compassionate release for inmates serving unusually long sentences would benefit the BOP because “aging, unhealthy inmates consume a disproportionate share of BOP’s scarce resources, which has cascading effects on federal prison operations and the safety and security of BOP staff, as well as inmates… [a]nd the thousands of prisoners potentially eligible for compassionate release who are serving ‘unusually long sentence[s]’ with ‘gross disparity…’ are especially likely to become elderly and unhealthy or disabled in prison.”
United States v. Bricker, Case No. 24-3286, 2025 U.S.App. LEXIS 9538 (6th Cir. April 22, 2025)
Fernandez v. United States, Case No. 24-556 (certiorari granted May 23, 2025)
Rutherford v. United States, Case No. 24-820 (petition for certiorari pending)
Brief of Amici Curiae Former Bureau of Prisons Officials In Support of Petitioner, Rutherford v. United States (filed March 5, 2025)
– Thomas L. Root