We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

COURT ORDERS BOP TO HONOR SETTLEMENT, WHILE INMATE COVID CASES INCREASE 30% IN ONE WEEK
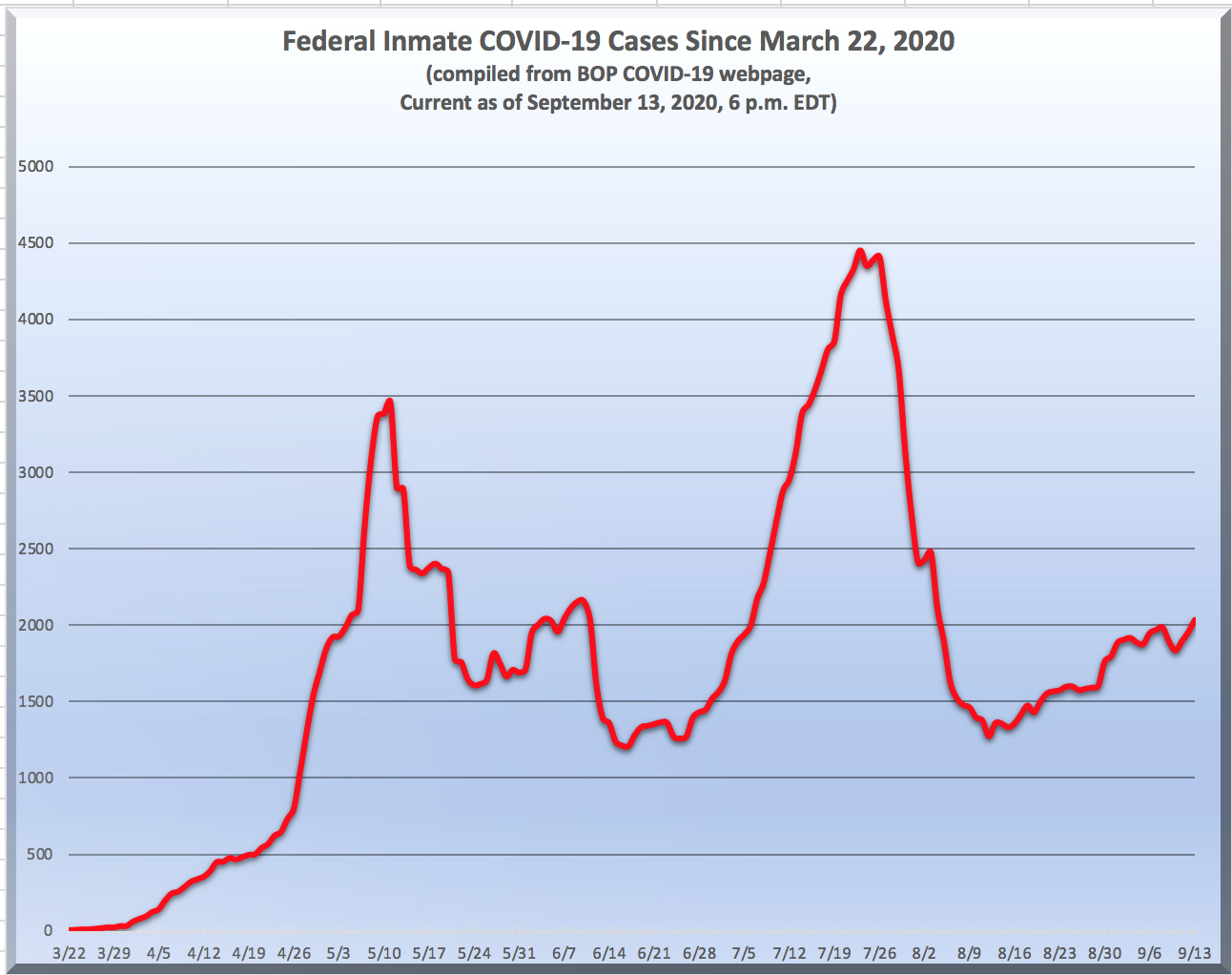
Ten days ago, the number of Bureau of Prisons inmate COVID-19 cases passed 5,000. That was a first… but it was nothing compared to last week.
As of last Friday, the BOP reported 7,278 ill inmates (a 30% from the week before),1,716 sick staff (up 9% from last week), COVID-19 in 127 BOP facilities and 167 dead inmates. The BOP has tested 58% of all inmates at least once, with the positivity rate continuing to ratchet up. As of last Friday, 34% of all inmate tests are positive for COVID.
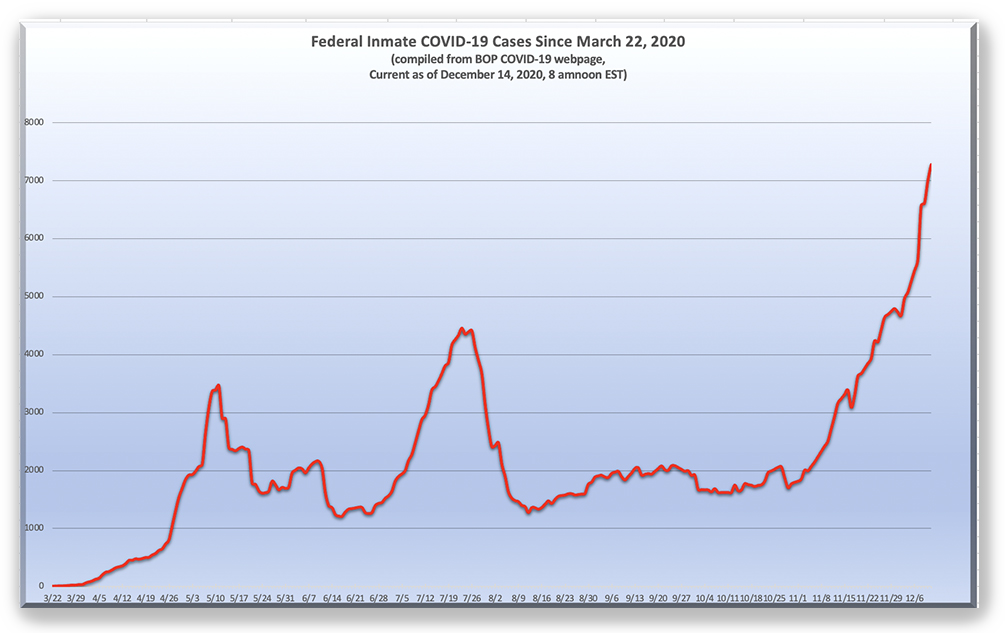
Recall that on December 2, BOP Director Michael Carvajal told a House Subcommittee that the BOP’s COVID-19 “procedures have proven effective as this is evidenced by the steep decline in our inmate hospitalizations, inmates on ventilators and deaths.” Some feel differently.
Last Friday, a Connecticut U.S. District Court found that the BOP had violated its settlement agreement in a class action of 450 medically vulnerable prisoners brought last spring over COVID-19 conditions at FCI Danbury. The unhappy judge ordered the BOP to release 17 medically vulnerable inmates by 5 p.m. the next day (a Saturday), prohibited the BOP from relying on administrative roadblocks to delay the release of those granted home confinement, and directed the BOP to report to the plaintiffs’ attorneys whenever the agency expects to fail to release inmates granted CARES Act home confinement within 14 days of grant.
The court order followed a long hearing the day before, where the court heard about a new Danbury COVID-19 outbreak and the BOP’s corresponding failure to mitigate the spread of the disease. In one week, the number of Danbury COVID-19 cases went from zero to nearly 50. The plaintiffs said despite the BOP’s promise to check daily for symptoms for the duration of the pandemic, the BOP failed to follow this pledge for two weeks during a surge of the disease around the country.
A July settlement of the lawsuit required the BOP to promptly identify prisoners who are low security risks and have a greater chance of developing serious complications from the virus and release them to home confinement. The settlement called for prisoners to be released within 14 days of being approved. But the plaintiffs’ lawyers say some of them have been waiting nearly three months to be released after being approved for home confinement.
 The BOP cited several reasons for the delays in releasing the inmates, including required 14-day quarantines due to the virus and BOP guidelines in releasing inmates to the community. The Court was not impressed.
The BOP cited several reasons for the delays in releasing the inmates, including required 14-day quarantines due to the virus and BOP guidelines in releasing inmates to the community. The Court was not impressed.
Meanwhile, in Minnesota, the ACLU last week filed suit alleging the BOP’s FCI Waseca has “failed to respond in any meaningful way to the pandemic.” The ACLU says the prison did not release medically vulnerable people from the prison, where two out of three inmates contracted COVID-19, making social distancing impossible.
New Jersey congressional leaders last week renewed their call to end inmate transfers to FCI Fort Dix. Led by Senators Robert Menendez and Cory Booker (both D-New Jersey), the state’s congressional delegation sent a second letter to BOP Director Carvajal week calling for the end of inmate transfers and asking the BOP to outline its plan for allocating and administering the COVID vaccine.
The BOP had previously instituted a moratorium on all inmate transfers to Ft Dix through Nov. 23 as active cases hit 300. The lawmakers and BOP staff have pointed to the October transfer of inmates from FCI Elkton to Ft Dix as the cause of the outbreak. BOP officials have denied the accusation. The moratorium was not extended, the BOP said last week, despite a previous letter from the state’s lawmakers demanding the moratorium continue until there are no active cases at the prison.
“By resuming transfers of incarcerated individuals into and out of the facility in the midst of a severe outbreak, BOP is putting at risk the lives of both staff and incarcerated individuals,” the lawmakers wrote in the letter.
 The BOP is seeing a resurgence of COVID at institutions where it had previously been controlled. The virus is again at FCC Lompoc, site of one of the worst prison COVID outbreaks in the country, according to the Santa Barbara Independent. An investigation last summer by the Dept. of Justice Inspector General found that the BOP’s initial response to COVID “failed on a number of fronts and likely contributed to the severity of the outbreak, including staffing shortages, inadequate screenings, and a scarcity of protective equipment.”
The BOP is seeing a resurgence of COVID at institutions where it had previously been controlled. The virus is again at FCC Lompoc, site of one of the worst prison COVID outbreaks in the country, according to the Santa Barbara Independent. An investigation last summer by the Dept. of Justice Inspector General found that the BOP’s initial response to COVID “failed on a number of fronts and likely contributed to the severity of the outbreak, including staffing shortages, inadequate screenings, and a scarcity of protective equipment.”
As of Friday, Englewood and Loretto each have more than 600 sick inmates, Texarkana and Pekin more than 300 each, five more facilities with more than 200, and 12 more BOP institutions with over 100 active COVID cases.
When a local newspaper asked the BOP about Loretto, a spokesman said the prisons are following accepted guidelines. While declining to address the Loretto situation “due to privacy, safety and security reasons,” the spokesman told the paper, “we can tell you all institutions have areas set aside for quarantine and medical isolation.”
Meanwhile, The New York Times last week criticized the BOP for its management of COVID at FDC Brooklyn. Noting that 55 inmates had tested positive for COVID-19, The Times said, “many months into this pandemic, the Federal Defenders of New York, a legal advocacy group, said officials at the jail aren’t following basic public health guidelines to prevent the spread of the virus, to care for sick inmates or to protect those who are most vulnerable. The reports… are disturbing. Corrections officers, they say, aren’t properly wearing masks, including while interacting with inmates. Sick inmates aren’t receiving proper medical attention and are being placed in cells with healthy individuals. One person incarcerated at the facility told an attorney with the Federal Defenders that severely ill inmates who asked for medical attention didn’t get it.”
A BOP spokesman disputed the Defenders’ claims. Nevertheless, the Times said, “if the conditions are anything like what the Federal Defenders describe, they are an affront to human dignity and a threat to the public health of Americans in and out of the Brooklyn facility.”
 And here’s an interesting glimpse at the BOP’s record-keeping, a factoid that could suggest to reasonable people that the BOP’s numbers cannot necessarily be trusted. A Youngstown, Ohio, news website, reporting on Columbiana County, Ohio, COVID numbers, was trying to derive a number of people recovered from the virus. It noted that FCI Elkton – located in the county – reported “896 incarcerated people and 54 employees had recovered from COVID-19 as of today… That number has declined in recent weeks, suggesting the bureau removes cases from its total when people are transferred out of the prison.”
And here’s an interesting glimpse at the BOP’s record-keeping, a factoid that could suggest to reasonable people that the BOP’s numbers cannot necessarily be trusted. A Youngstown, Ohio, news website, reporting on Columbiana County, Ohio, COVID numbers, was trying to derive a number of people recovered from the virus. It noted that FCI Elkton – located in the county – reported “896 incarcerated people and 54 employees had recovered from COVID-19 as of today… That number has declined in recent weeks, suggesting the bureau removes cases from its total when people are transferred out of the prison.”
Yale University Law School, CJAC Wins Speedy Release of Medically Vulnerable Individuals from Federal Prison in Danbury (December 12, 2020)
Order, Whitted v Easter, Case No 3:20-cv-00569 (D. Conn, December 11, 2020)
WWLP-TV, Judge orders release of 17 virus-vulnerable federal inmates (December 12, 2020)
KMSP-TV, ACLU sues federal prison in Waseca, Minn. after 67% of inmates test positive for COVID-19 (December 10, 2020)
Burlington County Times, More NJ lawmakers renew call for end to inmate transfers at FCI Fort Dix (December 10, 2020)
Johnstown Tribune-Democrat, Feds: Loretto prison following guidelines (December 11, 2020)
Mahoning Matters, Columbiana County reports 244 new COVID-19 cases, 2 new deaths (December 11, 2020)
New York Times, Stop the Coronavirus Outbreak at Brooklyn’s Federal Jail (December 8, 2020)
– Thomas L. Root


 The IG said that because of operational deficiencies at USP Atlanta and MCC New York (which has since been closed), its investigators set out to “assess how critical issues at BOP institutions are identified, communicated to BOP Executive Staff, and remediated.”
The IG said that because of operational deficiencies at USP Atlanta and MCC New York (which has since been closed), its investigators set out to “assess how critical issues at BOP institutions are identified, communicated to BOP Executive Staff, and remediated.”