We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

FIVE YEARS SHOULD BE LONG ENOUGH TO GET FIRST STEP ACT RIGHT
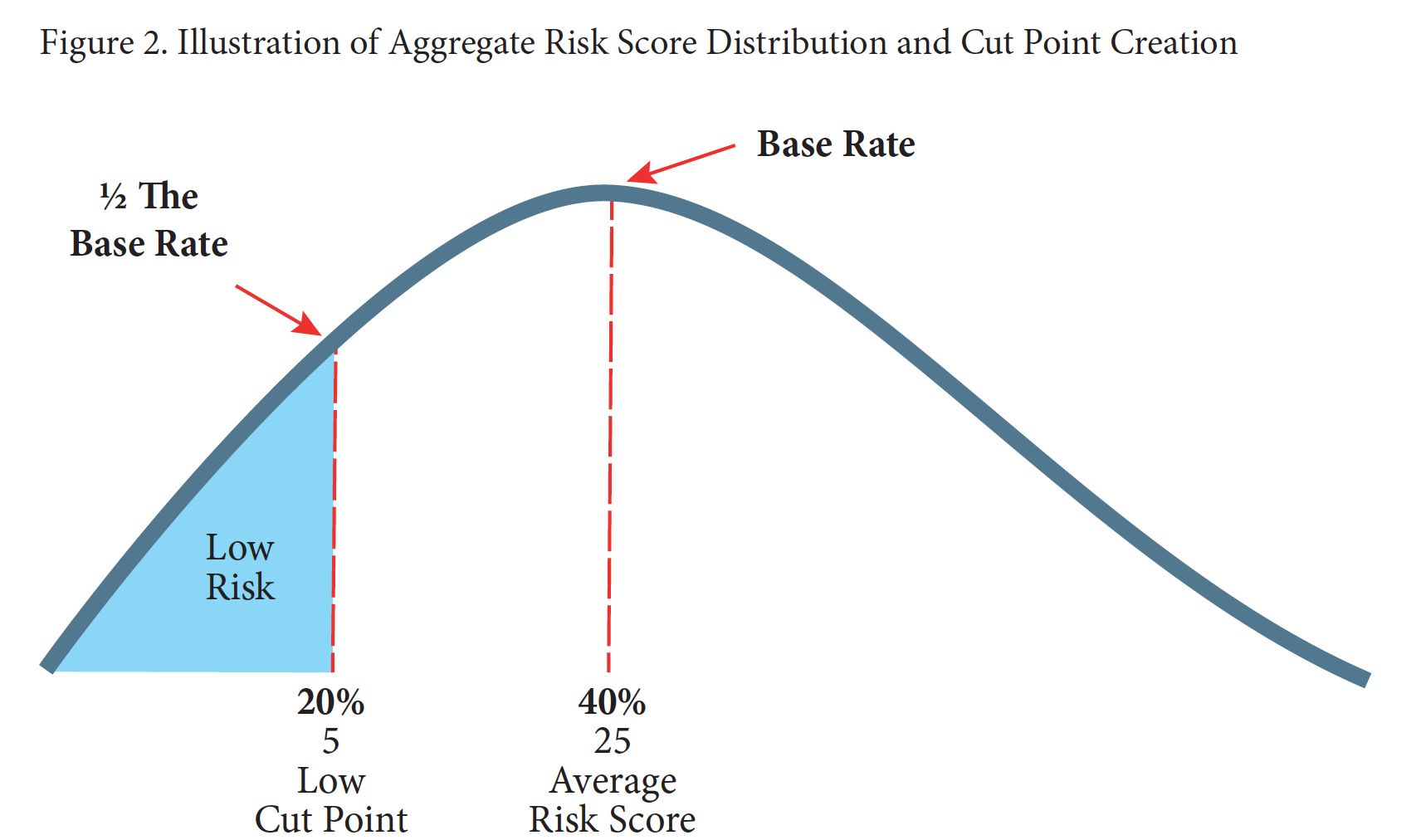
 The First Step Act, including its innovative system for granting credits to inmates who complete programs designed to reduce recidivism, is 5 years old in less than two months. But it took three years of fits and starts before the Bureau of Prisons pretty much had a final set of rules for administering FSA credits (after a proposal that was as miserly as the final rule was generous hanging around for a year of comments).
The First Step Act, including its innovative system for granting credits to inmates who complete programs designed to reduce recidivism, is 5 years old in less than two months. But it took three years of fits and starts before the Bureau of Prisons pretty much had a final set of rules for administering FSA credits (after a proposal that was as miserly as the final rule was generous hanging around for a year of comments).
Now, almost two years later, the BOP is still muddled in trying to launch a computer program of forward-looking calculation for FSA credits that predicts when a prisoner will leave BOP custody for halfway house or home confinement (HH/HC). The agency still lacks a comprehensive list of what types of inmate employment or education constitutes “productive activities,” which are supposed to continue a prisoner’s earning of FSA credits. And the BOP continues to deny HH/HC placement because it lacks resources, despite First Step’s requirement that inmates be placed to the full extent of their FSA credits.
Writing in Forbes last week, Walter Pavlo observed that “prisoners, mostly minimum and low security, who are eligible for these credits have done their best to try to participate in programs but many complain of a lack of classes, mostly due to the challenges the BOP is having in hiring people. However, beyond that, the BOP has been liberal in accepting that the BOP does not have the staff to fulfill the demand for classes and credits are being given anyway, mostly for participating in productive activities, like jobs. This misses the primary mission of programming meant to have a lasting, positive influence on prisoners after they leave the institution.
“Now,” Pavlo said, “nearly two years since the Federal Register’s Final Rule in January 2022, the BOP still has no reliable calculator to determine the number of FSA credits a prisoner will earn during a prison term… One of the last remaining issues is for the BOP to have a forward-looking calculation for FSA credits that predicts when a prisoner will leave BOP custody. It sounds easy, but the BOP’s current computer program can only assess credits after they are earned each month, and it usually takes a full month after they are earned for them to post. The result is that each month, prisoners’ families look at BOP.gov to see if there are indeed new credits and if the amount they are expecting matches what is expected. This moving date is important because it can also determine when prisoners can leave prison for home confinement or halfway house. The result, prisoners are staying in institutions, institutions that are understaffed, for days, weeks and months beyond when they could be released to home confinement or halfway houses. This is defeating one of the other initiatives of the First Step Act and that was to get more people out of decaying BOP facilities and into another form of confinement that is far less expensive.”

First Step is important to Congress. When BOP Director Colette Peters appeared for a Senate Judiciary Committee oversight hearing chaired by Senator Richard Durbin (D-IL) last month, “her answer failed to address the continued shortcomings of the implementation,” Pavlo said. “There are thousands of prisoners, many minimum security, who are stuck in prison because of a lack of a computer program that simply calculates forward-looking FSA credits…This computer program was actually alluded to in declarations the BOP submitted to federal courts in 2022 stating that it would be implemented ‘soon.’ Over a year since those declarations, there is still no program to accurately calculate when a prisoner will leave an institution.”
The BOP is facing a substantial halfway house bed shortage as well. There is also the issue of insufficient halfway house space. Unlike HH/HC placement for prisoners without FSA credits, 18 USC 3624(g)(2) does not give the BOP discretion. Subsection 3624(g)(2) says that if a prisoner is eligible (has FSA credits not already applied to a year off of the sentence), he or she “shall be placed in prerelease custody as follows,” describing halfway house or home confinement. There’s nothing hortatory about it. The BOP is required to put the prisoner in HH/HC. Excuses not accepted.
 Pavlo argued that “the only way to address this situation is to implement a task force to move prisoners through the system and catch up from the failures of the past few years. Systemic challenges of shortages of staff and augmentation which takes away staff like case managers from their jobs, cause continued problems. The BOP needs to get caught up, move prisoners along and develop reliable systems that will assure that the FSA is implemented as the law requires. While the BOP has made great strides, these last challenges of full implementation can be achieved by focusing a concerted effort on three issues; fixing the calculator, assessing the prisoners who will soon be going home as a result of that computer fix, and expanding halfway house capacity to handle them.”
Pavlo argued that “the only way to address this situation is to implement a task force to move prisoners through the system and catch up from the failures of the past few years. Systemic challenges of shortages of staff and augmentation which takes away staff like case managers from their jobs, cause continued problems. The BOP needs to get caught up, move prisoners along and develop reliable systems that will assure that the FSA is implemented as the law requires. While the BOP has made great strides, these last challenges of full implementation can be achieved by focusing a concerted effort on three issues; fixing the calculator, assessing the prisoners who will soon be going home as a result of that computer fix, and expanding halfway house capacity to handle them.”
Forbes, Time For A Bureau Of Prisons Task Force To Implement The First Step Act (October 16, 2023)
– Thomas L. Root