We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

THE INCREDIBLE SHRINKING COMMUTATION
As has been his recent habit, President Joe Biden capped off Second Chance Month yesterday by granting clemency to a whopping 16 people. Of these, 11 were pardons of people who have been out of prison for an average of about 20 years. Only five were commutations of people currently serving sentences, and of the five, a total of zero will walk out of prison today.

Biden said in a statement that many of the people getting clemency had received “disproportionately longer” sentences than they would have under current law. The White House clemency list made a point of that, too, although the relevance of that to a pardon of someone who’s been out for 20 years is dubious.
The Associated Press said Biden “is grappling with how to boost support from communities of color that heavily supported him over Republican Donald Trump in the 2020 election.”
Biden trumpeted that “[l]ike my other clemency actions, these pardons and commutations reflect my overarching commitment to addressing racial disparities and improving public safety.”
Overaching commitment? Biden, who promised during his 2020 campaign to reform the federal clemency system, has done slightly better than President Trump, a pretty low bar. At this point in his presidency, Trump had pardoned 28 to Biden’s 24, but only commuted sentences on 11 to Biden’s 129. At this point in his first term, President Obama had pardoned 39 to Biden’s 24, but only commuted the sentence of a single inmate.
Of course, by the time he was done, Obama had granted commutations to 1,712 prisoners.
Biden apparently didn’t find as many commutation petitions to love as he did during last year’s Second Chance Month, when he granted commutations to 31 people. This year, he said the five who had their sentences commuted “have shown that they are deserving of forgiveness and the chance at building a brighter future for themselves beyond prison walls.”
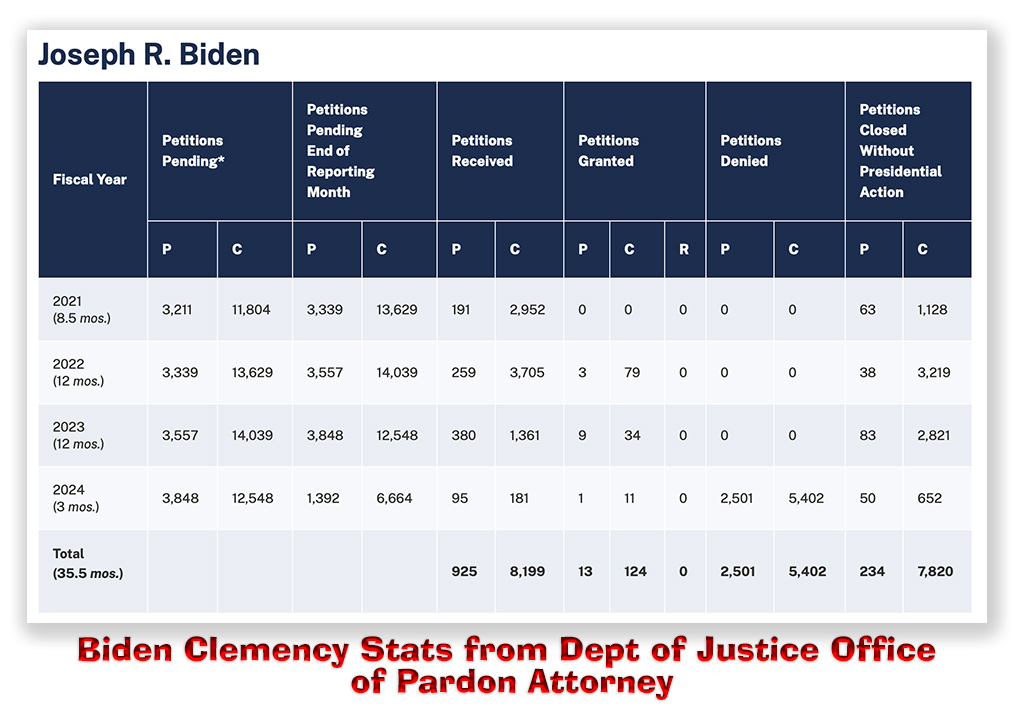
He didn’t think the same of the 2,501 pardon and 5,402 commutation petitions he has quietly denied in the last six months.
What’s more, Biden’s commutations have fallen from 79 in Fiscal Year 2022 (October 2021-September 2022) to 34 in FY 2023 and only 16 in the first half of FY 2024. He is not likely to grant any clemency in the remainder of this Fiscal Year.
 By the numbers, over the last six months, a prisoner’s commutation petition had a 44.77% chance of being denied, a 55.19% of not being acted on, but only a 0.04% chance of being granted.
By the numbers, over the last six months, a prisoner’s commutation petition had a 44.77% chance of being denied, a 55.19% of not being acted on, but only a 0.04% chance of being granted.
At least in Vegas, when the house gives you odds like that, it usually comps you drinks.
Associated Press, Biden pardons 11 people and shortens the sentences of 5 others convicted of non-violent drug crimes (April 24, 2024)
The White House, Clemency List (April 24, 2024)
The White House, Statement from President Joe Biden on Clemency Actions (April 24, 2024)
– Thomas L. Root