We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

THIS COMES AS NO SURPRISE
 The Department of Justice is interpreting the First Step Act in a way that keeps more inmates serving crack sentences behind bars longer, even as President Trump touts his administration’s role in passage of First Step, the law that made crack-cocaine sentence relief available to pre-Fair Sentencing Act defendants.
The Department of Justice is interpreting the First Step Act in a way that keeps more inmates serving crack sentences behind bars longer, even as President Trump touts his administration’s role in passage of First Step, the law that made crack-cocaine sentence relief available to pre-Fair Sentencing Act defendants.
The Washington Post report last week confirmed what most people already know (and what Reuters reported several months ago), that DOJ is arguing that a defendant’s sentence length, when resentenced under the Fair Sentencing Act, should be based on the amount of crack cocaine that his or her Presentence Report found the defendant actually possessed or trafficked, rather than the amount stated in the indictment and which the jury found or the defendant pled. The Post reported that federal prosecutors have made the argument in hundreds of cases.
The distinction is crucial. The amount of crack specified in the indictment must be proven by the government to a jury. The presentence report, on the other hand, is a loosey-goosey collection of the prosecution’s version of the offense and all of the collected but unsubstantiated law enforcement gossip about the defendant that makes him or her look even worse than reality does. The standard of proof is low, the procedures amorphous, and the judge all too willing to not decide evidentiary disputes because they simply do not matter to the court in the sentencing process.
 As a result, while a defendant may have been found guilty of the offense in the indictment, for instance, distribution of more than 50 grams of crack, the presentence report may cite “reliable sources” who say the defendant possessed maybe a gram a week for two years. The presentence report does some simple addition, and a total of 730 grams results.
As a result, while a defendant may have been found guilty of the offense in the indictment, for instance, distribution of more than 50 grams of crack, the presentence report may cite “reliable sources” who say the defendant possessed maybe a gram a week for two years. The presentence report does some simple addition, and a total of 730 grams results.
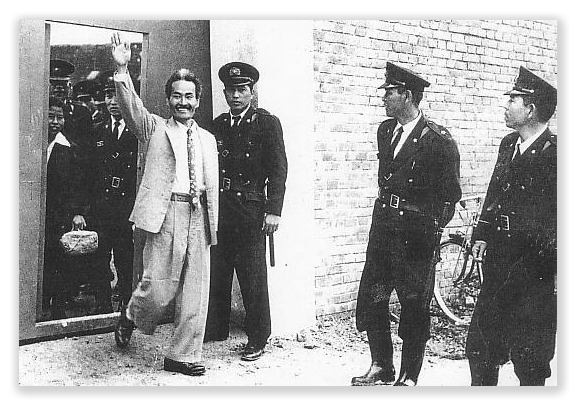
The Post said DOJ was even seeking to reincarcerate some people already released under the retroactive FSA. One targeted former inmate was Gregory Allen, who appeared at a White House event in April to celebrate passage of the law. President Trump even called Greg to the microphone.
Before the White House event, prosecutors had lost their bid to keep Allen behind bars. Even as the President asked Greg to speak, the government was appealing its loss. DOJ dropped its appeal about two weeks after Greg’s appearance.
A DOJ spokesman defended the department’s First Step interpretation in an interview with the Post. He said DOJ’s position was justified because prosecutors in years past didn’t need to prove large amounts of drugs to obtain long prison sentences. Under today’s sentencing regime, prosecutors would likely charge the offenders with having larger drug quantities, DOJ hypothesizes. “The government’s position is that the text of the statute requires courts to look at the quantity of crack that was part of the actual crime,” the spokesman argued. “This is a fairness issue.”
Judges have rejected the DOJ interpretation in a majority of cases reviewed by the Post. But at least five federal judges have agreed with the DOJ interpretation, and others have withheld judgment until appeals courts decide the issue.
In the weeks after the bill became law, many AUSAs allowed inmate petitions for early release to go unchallenged. Then, at the direction of the DOJ, prosecutors began to reverse course, court records show. In March, AUSA Jennifer Bockhorst of ND WVa asked federal judges to place a hold on more than two dozen applications for relief, some of which she had not previously opposed. She wrote that she expected to oppose at least some of those applications based on new guidance from the Justice Department.
Some of the people who helped write the legislation also disagree, including Brett Tolman, a former US attorney in Utah. He notes that the First Step text does not explicitly instruct courts to consider the actual amount of crack an offender allegedly had. “This is not a faithful implementation of this part of the First Step Act,” Tolman told the Post. “At some point, they figured out a way to come back and argue that it wouldn’t apply to as many people.”
Rep. Jerrold Nadler (D-New York), chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, accused DOJ at a congressional hearing last month of “trying to sabotage” the law by interpreting it in this way.
Attorney General Barr has reportedly worried that early releases of inmates under the law will increase crime. Anonymous officials told the Post that Barr is concerned the administration will be blamed if crime increases.
A great example of the kind of blame the AG hoped to duck is illustrated by the person of Rhode Island defendant Joel Francisco, released earlier under First Step this year after 14 years into a life sentence for selling crack. We previously reported he was on the run after being charged with a murder. He has since been arrested, and last week, CNN made his crime a national story.
Also last week, a routine resentencing in Connecticut made national headlines, when Joel Soto’s 17-year sentence was cut to time served, under the lurid headine, “‘Joe Crack’ asks for reduced sentence in drug case.”
“More than 4,700 inmates have been released from prison under the law since its signing late last year,” CNN reported, “and federal officials believe Francisco is the first among them to be accused of murder. While an outlier, his case is raising questions and resurfacing concerns from detractors of the legislation.”
“ This case is upsetting but it’s not a surprise,” said Sen. Tom Cotton (R-Arkansas), one of First Step’s biggest critics on Capitol Hill. “Letting violent felons out of prison early as the First Step Act did leads to more crime and more victims.”
This case is upsetting but it’s not a surprise,” said Sen. Tom Cotton (R-Arkansas), one of First Step’s biggest critics on Capitol Hill. “Letting violent felons out of prison early as the First Step Act did leads to more crime and more victims.”
Other lawmakers who supported the bill called the incident a tragedy, but hoped that it wouldn’t stand in the way of more progress. “If you’re looking at reforming the criminal justice system you cannot pick an individual criminal act to then raise the question as to whether or not you do reforms to the system,” said Rep. Karen Bass (D-California), a member of the House Judiciary Committee and the chair of the Congressional Black Caucus.
None of this should surprise anyone. Despite the First Step Act rhetoric, The New York Times reported last week that despite bipartisan calls to treat drug addiction as a public health issue rather than as a crime — and despite the legalization of marijuana in more states — arrests for drugs increased again last year. Such arrests have increased 15% since Trump took office.
Washington Post, Crack cocaine quantities at issue as DOJ opposes some early releases under First Step Act (Nov. 7)
ABA Journal, Crack cocaine quantities at issue as DOJ opposes some early releases under First Step Act (Nov. 8)
CNN, He was one of the first prisoners released under Trump’s criminal justice reform law. Now he’s accused of murder (Nov. 9)
Newport News, Virginia, Daily Press, ‘Joe Crack’ asks for reduced sentence in drug case (Nov. 2)
The New York Times, Is the ‘War on Drugs’ Over? Arrest Statistics Say No (Nov. 5)
– Thomas L. Root


 The BOP’s CARES Act authority to place inmates in home confinement expires, according to the law, 30 days after the end of the national pandemic emergency. That emergency was originally declared by President Trump and extended by President Biden. Biden’s last extension was set to expire March 1, 2022, by operation of 50 USC § 1622(d).
The BOP’s CARES Act authority to place inmates in home confinement expires, according to the law, 30 days after the end of the national pandemic emergency. That emergency was originally declared by President Trump and extended by President Biden. Biden’s last extension was set to expire March 1, 2022, by operation of 50 USC § 1622(d). What this means is the BOP’s authority to place people in home confinement under the CARES Act will continue for another year unless Attorney General Merrick Garland would decide the BOP no longer needs to decrease population. Given that the BOP must still absorb another 6,085 federal prisoners from private prisons, that inmate totals are trending upward again, and that the BOP is still understaffed, it is unlikely that the AG will abandon the CARES Act any time soon.
What this means is the BOP’s authority to place people in home confinement under the CARES Act will continue for another year unless Attorney General Merrick Garland would decide the BOP no longer needs to decrease population. Given that the BOP must still absorb another 6,085 federal prisoners from private prisons, that inmate totals are trending upward again, and that the BOP is still understaffed, it is unlikely that the AG will abandon the CARES Act any time soon.