We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

COVID-19 REALITY KICKS BOP, INMATES HARD
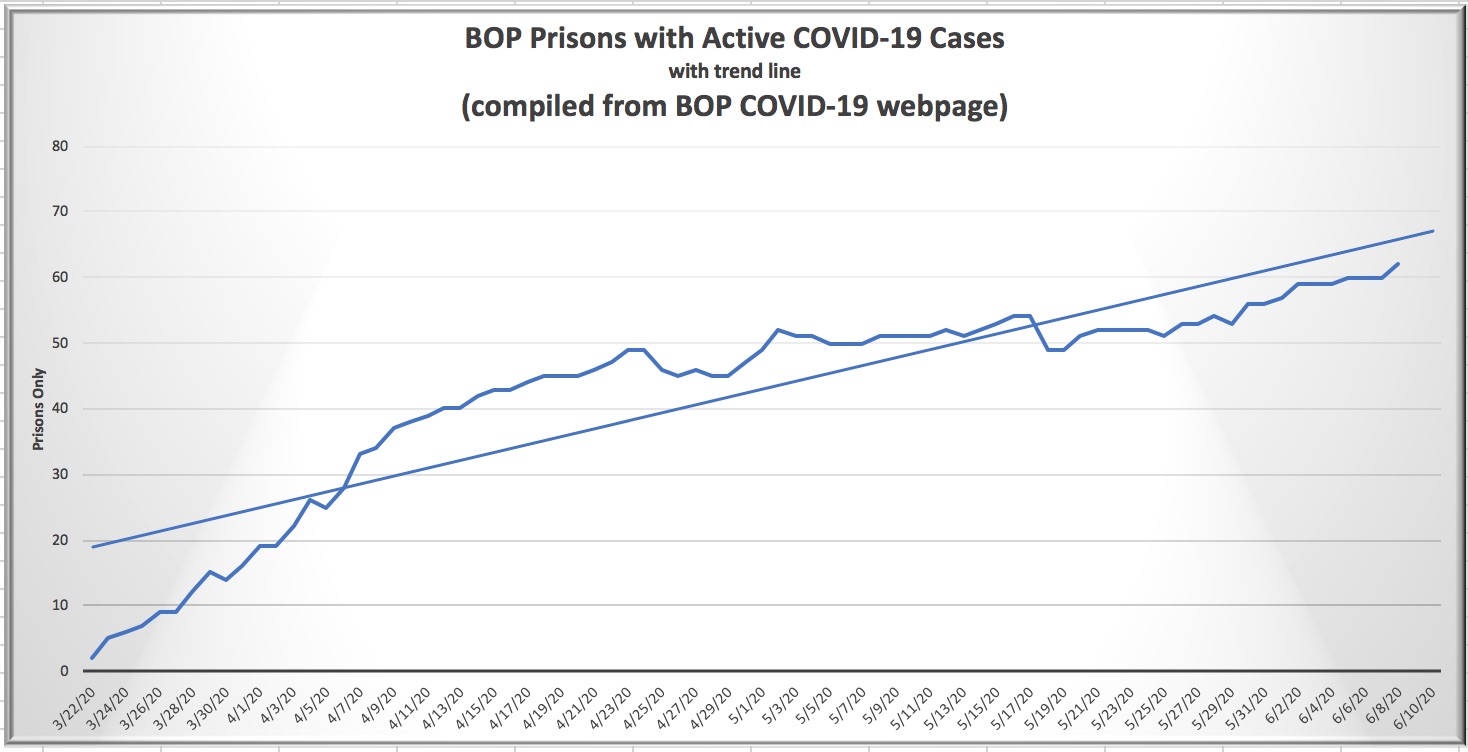
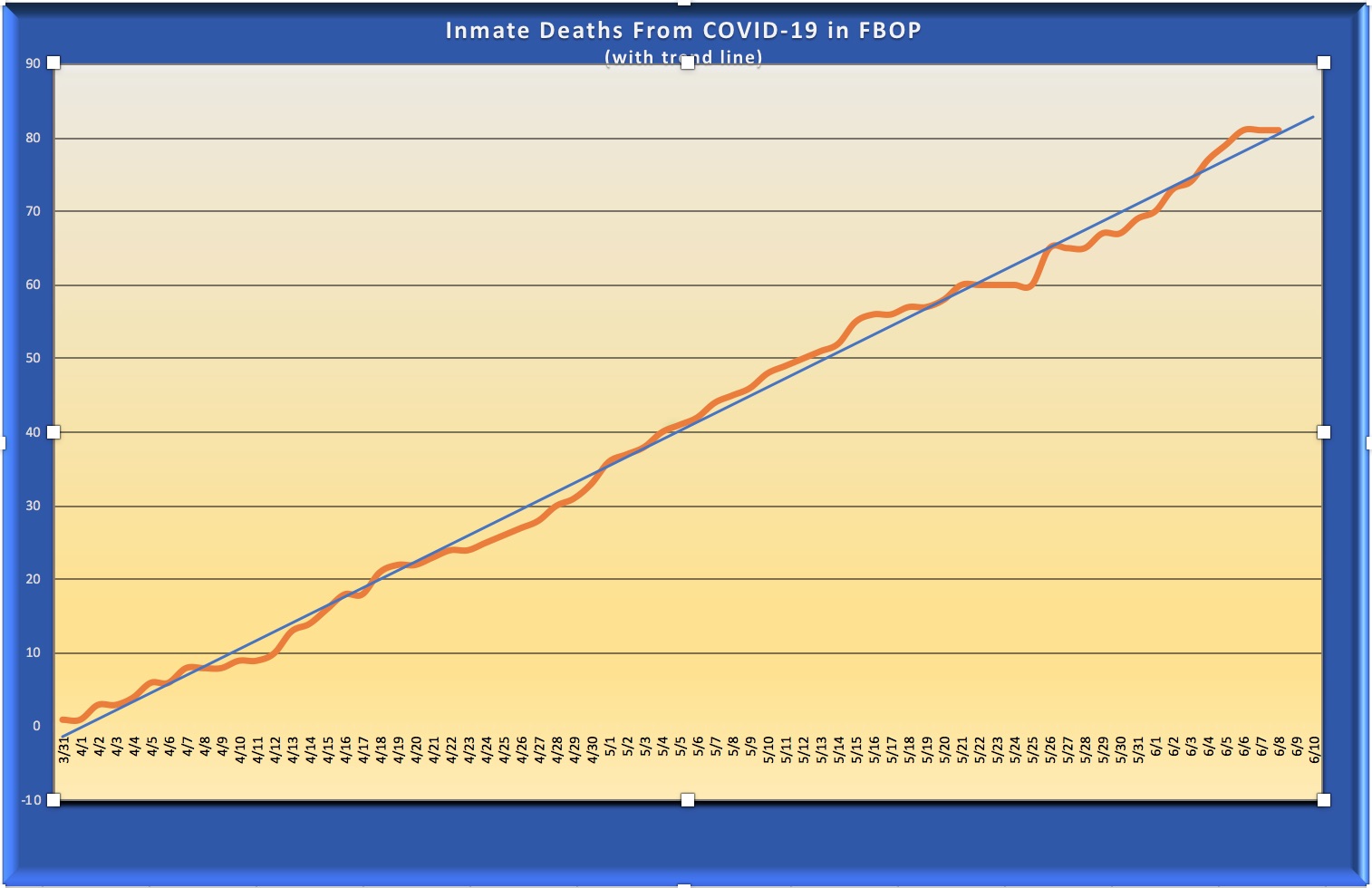
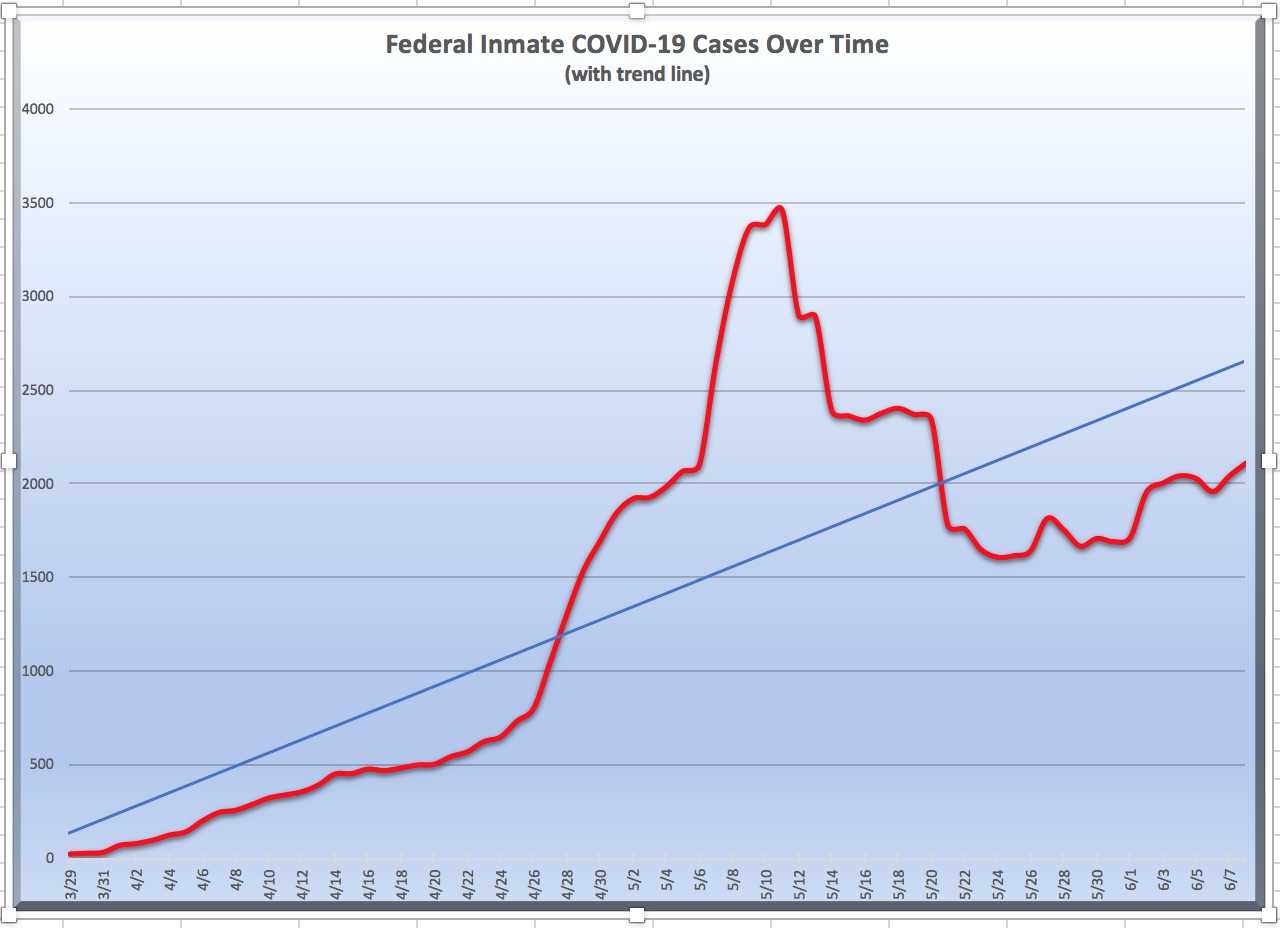
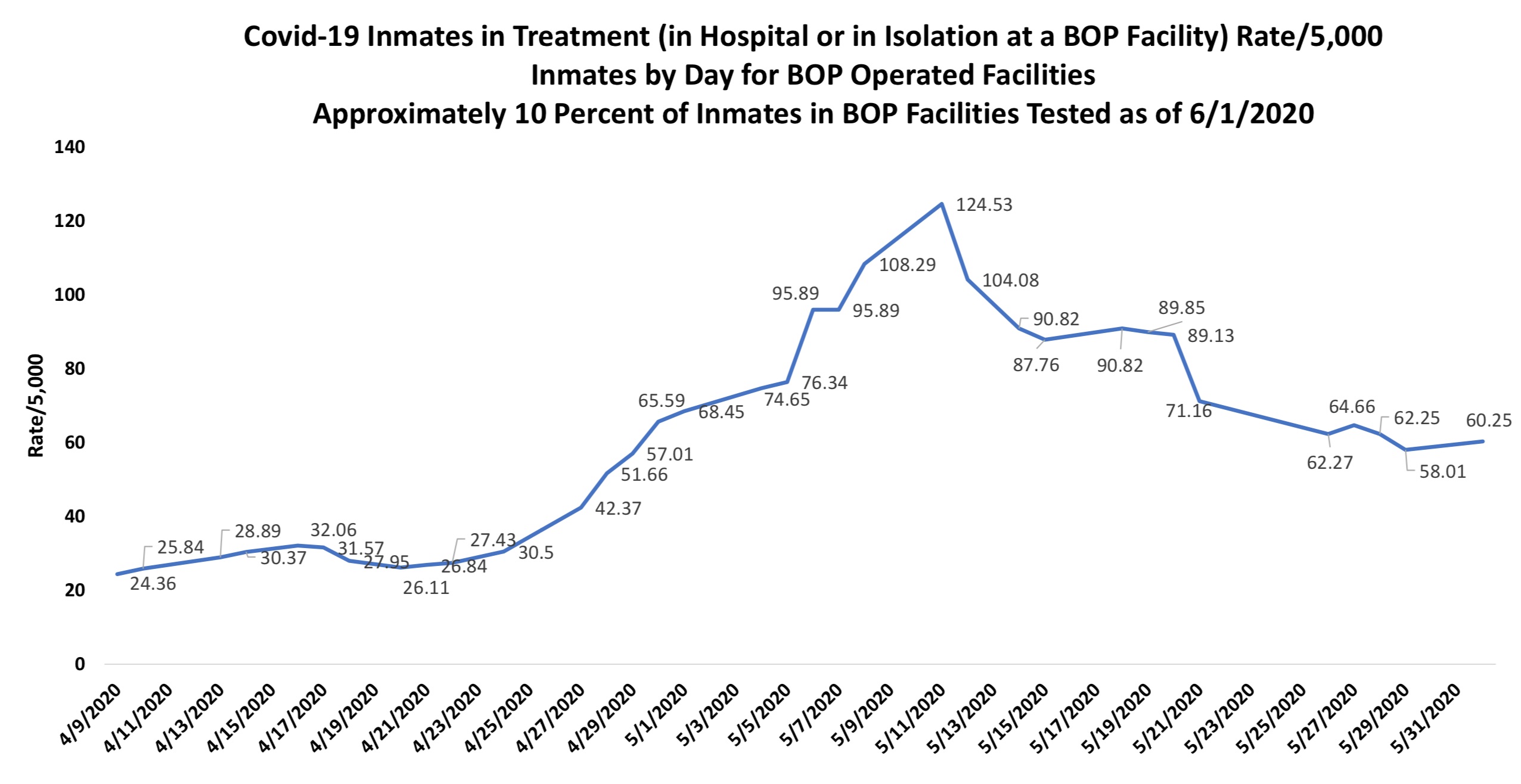
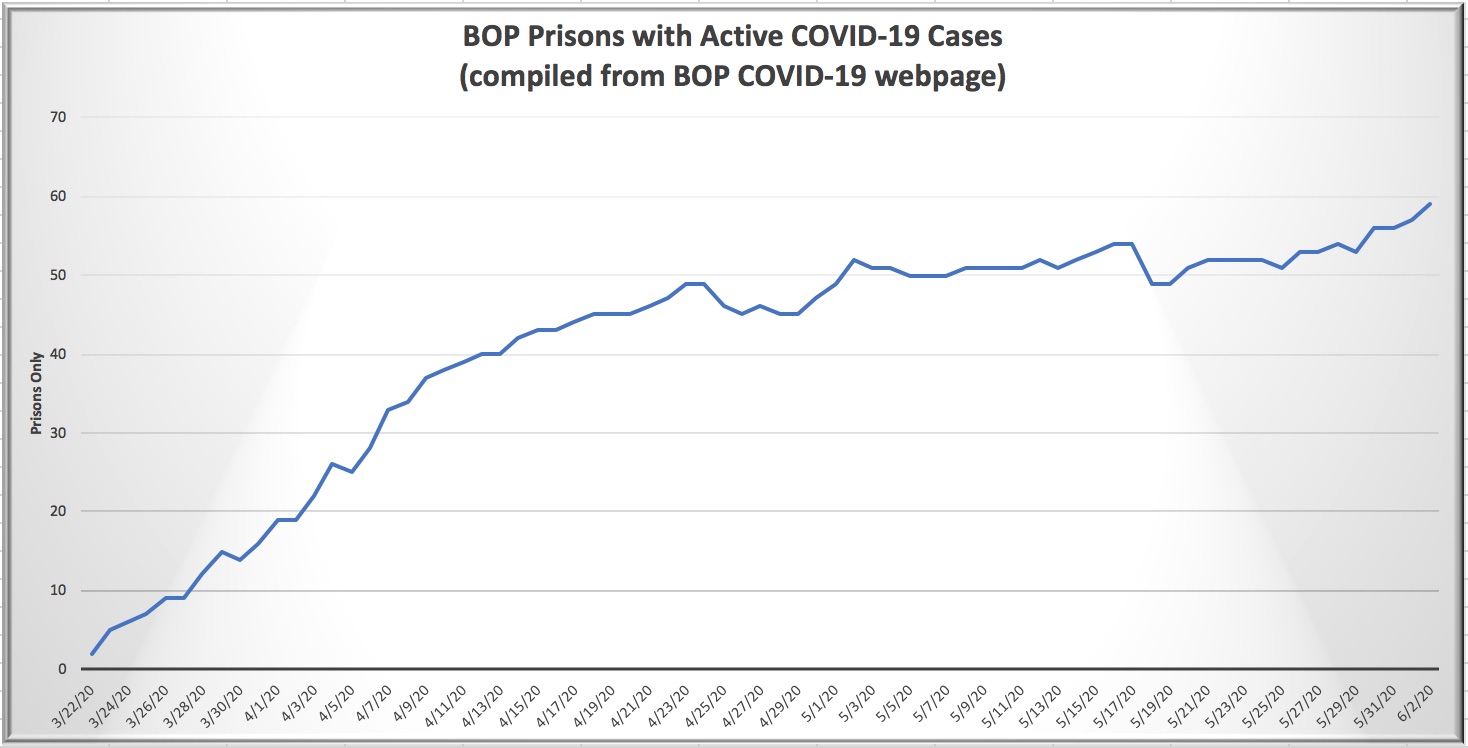
Two weeks ago, the Federal Bureau of Prisons had COVID-19 on the run. The number of infected inmates had been falling, falling, falling, throughout June, a real bear market for the virus. The number of sick inmates fell to 1,256 by June 25 from a high of 2,109 only 17 days before, staff infections had slipped to 133 from an early June high of 190, and the number of BOP facilities experiencing infections was holding steady at 70. Inmate deaths seemed to have peaked at 92.
 Two weeks later, that real-world pandemic you’ve been hearing about has kicked the BOP in the ass. As of late today, inmate infections are up 81% to 2,109, staff infections have increased by 59%, and the number of BOP facilities with the virus on premises hit 93 (that is, a whopping 76% of all BOP facilities). Six more inmates have died, bringing the total to 98.
Two weeks later, that real-world pandemic you’ve been hearing about has kicked the BOP in the ass. As of late today, inmate infections are up 81% to 2,109, staff infections have increased by 59%, and the number of BOP facilities with the virus on premises hit 93 (that is, a whopping 76% of all BOP facilities). Six more inmates have died, bringing the total to 98.
The BOP has been looking to tamp coronavirus outbreaks with testing, but testing is spotty. Overall, the BOP says it has tested 30,425 inmates, only about 23% of the BOP population. About 29% of the tests are coming back positive.
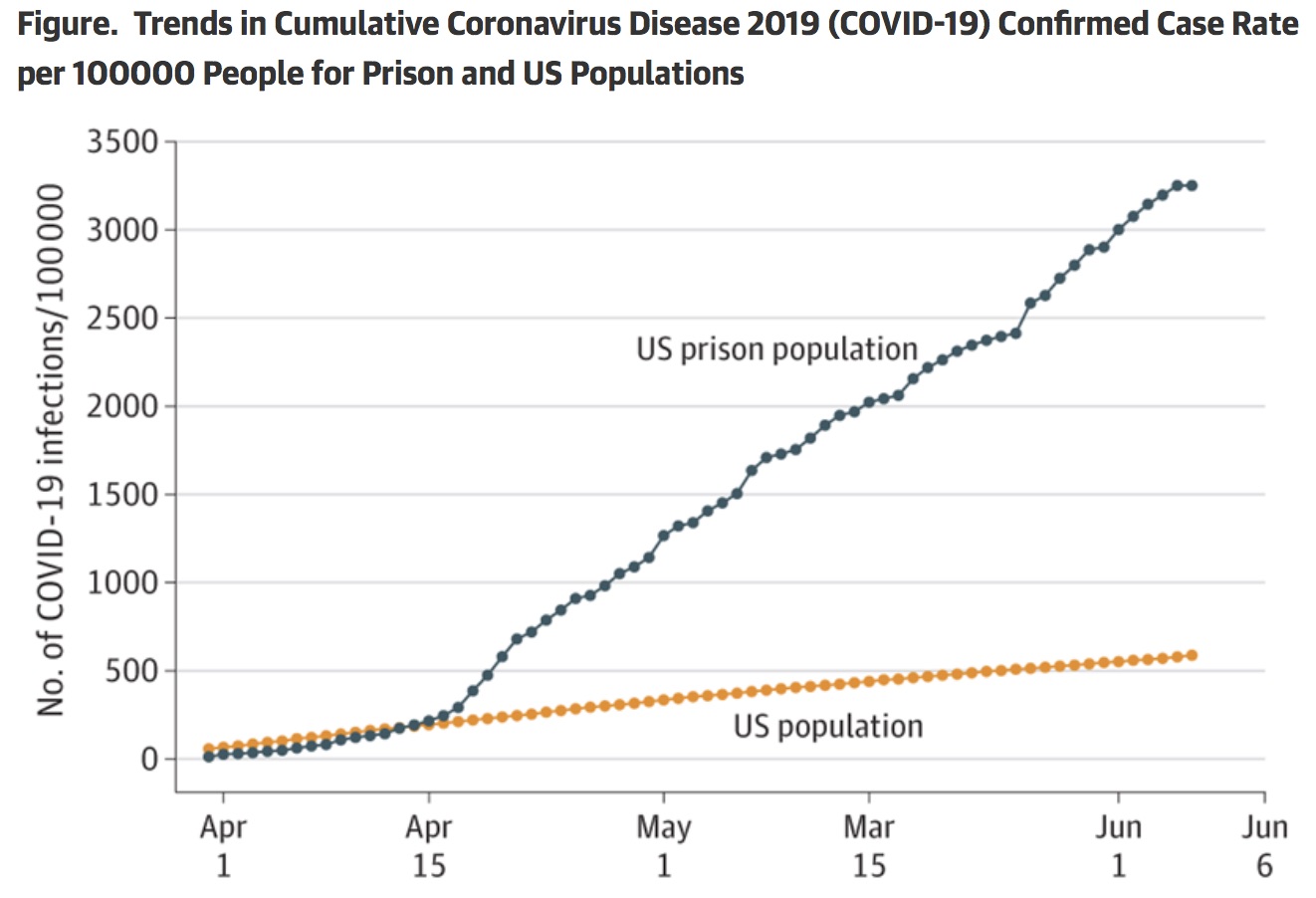
Meanwhile, an alarming report in the Journal of the American Medical Association today found that if coronavirus trotted through American society, it galloped through the prisons (see graph from the article, above). What’s more, the effects in prison were demonstrably worse. “The COVID-19 case rate for prisoners was 5.5 times higher than the U.S. population case rate of 587 per 100, 00” JAMA reported. “The crude COVID-19 death rate in prisons was 39 deaths per 100, 000 prisoners, which was higher than the U.S. population rate of 29 deaths per 100, 000 (Table).” And in a case of doing more with less, U.S. prisons managed to post this sadly impressive statistic despite the fact that in the general population, most of the deaths (81%) came from the cohort of people age 65 or older. But that group comprises 16% of the general population, but only 3% of prisoners. Even with all those extra old people in the general population, prisons managed to bury more COVID-19 victims per 100,000 than did society in general.
 The virus hasn’t peaked, but it is nevertheless safe to say that inmate class action suits against the BOP over the agency’s mismanaging of the COVID-19 pandemic has. Last week, the Massachusetts federal district court dismissed an inmate class action against FMC Devens after ruling that it could not proceed as a 28 USC § 2241 habeas corpus action. The inmate plaintiffs refused to proceed under the Prison Litigation Reform Act (which would have required each plaintiff to endure a six month-long administrative remedy process within the BOP before filing suit, thus dooming any hope for judicial relief while it could still do any good).
The virus hasn’t peaked, but it is nevertheless safe to say that inmate class action suits against the BOP over the agency’s mismanaging of the COVID-19 pandemic has. Last week, the Massachusetts federal district court dismissed an inmate class action against FMC Devens after ruling that it could not proceed as a 28 USC § 2241 habeas corpus action. The inmate plaintiffs refused to proceed under the Prison Litigation Reform Act (which would have required each plaintiff to endure a six month-long administrative remedy process within the BOP before filing suit, thus dooming any hope for judicial relief while it could still do any good).
In a Southern District of New York class action against MCC New York, the court denied the inmate plaintiffs a preliminary injunction based on 8th Amendment violations. The court agreed that “the inmates are likely to show that the MCC’s response to the pandemic was ad-hoc and overlooked many gaps in its scheme to identify and isolate infected inmates — creating conditions that posed a substantial risk to the health of all inmates,” but that they probably could not show that the MCC’s failures were a result of “deliberate indifference to their plight” as opposed to bumbling negligence.
In North Carolina, FCC Butner inmates voluntarily dismissed their lawsuit that aimed their 8th Amendment rights were being violated by the prison’s handling of the COVID-19 pandemic. U.S. District Court Judge Louise W. Flanagan denied the inmates’ motion for a temporary restraining order and preliminary injunction June 11.
 Nevertheless, an Oregon public defender filed suit last Tuesday alleging that “whether through indifference or incompetence, the Federal Bureau of Prisons is endangering the lives of individuals entrusted to its care by failing to establish consistent and effective safeguards to protect them from the coronavirus.” The suit targets FCI Sheridan, and was brought on behalf of a single inmate. Just in the past week, Sheridan reported its first COVID-19 case.
Nevertheless, an Oregon public defender filed suit last Tuesday alleging that “whether through indifference or incompetence, the Federal Bureau of Prisons is endangering the lives of individuals entrusted to its care by failing to establish consistent and effective safeguards to protect them from the coronavirus.” The suit targets FCI Sheridan, and was brought on behalf of a single inmate. Just in the past week, Sheridan reported its first COVID-19 case.
Journal of the American Medical Association, COVID-19 Cases and Deaths in Federal and State Prisons (July 8, 2020)
Fernandez-Rodriguez v. Licon-Vitale, 2020 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 116749 (S.D.N.Y. July 2, 2020)
Grinis v. Spaulding, Case No. 1:20cv10738 (D.Mass)
Wake Weekly, Butner Inmates Withdraw Lawsuit Over COVID-19 Response (July 2)
Oregon Public Broadcasting, Federal Lawsuit Calls Out COVID-19 Conditions at Sheridan Prison (June 30)
– Thomas L. Root