We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

9TH CIRCUIT ALLOWS FIRST STEP CHANGE IN § 924(c) STACKING TO SUPPORT COMPASSIONATE RELEASE
In 2007, Howard Chen was busted with a distribution-sized amount of MDMA in his car. Later, the DEA found more MDMA, two guns and cash at his house.
 A jury convicted Howie of six drug-related counts and two 18 USC § 924(c) counts for possessing a gun during and in furtherance of a drug crime. He got 48 months for the drug counts, 60 more months for the first gun offense and 300 months for the second one: a total of 34 years for a fairly garden-variety non-violent drug case.
A jury convicted Howie of six drug-related counts and two 18 USC § 924(c) counts for possessing a gun during and in furtherance of a drug crime. He got 48 months for the drug counts, 60 more months for the first gun offense and 300 months for the second one: a total of 34 years for a fairly garden-variety non-violent drug case.
In late 2020, Howard filed a motion for sentence reduction, seeking compassionate release for – among other reasons – that the First Step Act changed 18 USC § 924(c) so that he would not have to get a minimum of 300 months for the second gun charge. Although the change was not retroactive, Howie contended that the unfairness of how the 2007 version of the statute mandated 300 months but the current statute did not was an extraordinary and compelling reason for granting him a sentence reduction.
The district court denied the compassionate release motion, holding that because Congress did not make the 18 USC § 924(c) change retroactive, it could not be an extraordinary and compelling reason for grant of compassionate release under 18 USC § 3582(c)(1)(A).
Last week, the 9th Circuit reversed, holding that a district court may consider the First Step Act’s non-retroactive changes to sentencing law – in combination with other factors particular to the individual – when finding extraordinary and compelling reasons for a sentence reduction.
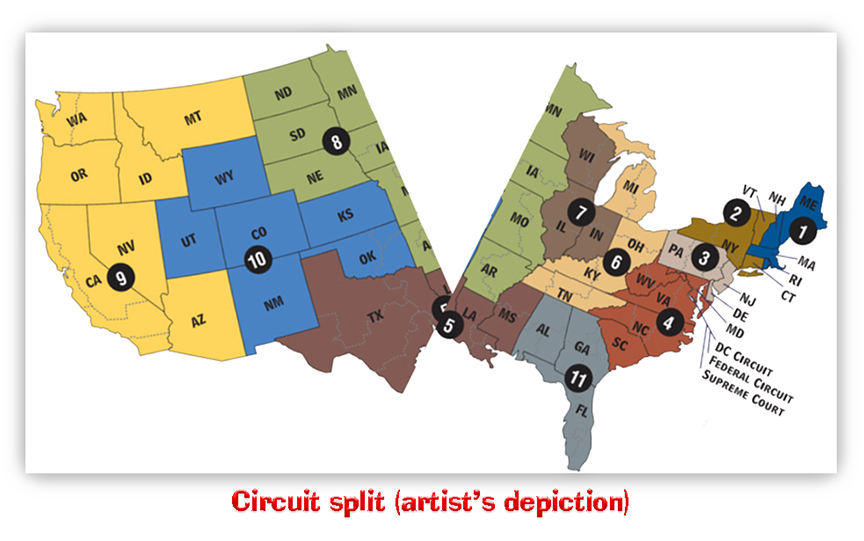
 Bloomberg said, “The opinion deepens a circuit split on the bipartisan 2018 reform law that has generated much litigation since then-President Donald Trump signed it.”
Bloomberg said, “The opinion deepens a circuit split on the bipartisan 2018 reform law that has generated much litigation since then-President Donald Trump signed it.”
The 3rd, 7th, and 8th Circuits have ruled that district courts may not consider non-retroactive sentence changes made by First Step, whether offered alone or in combination with other factors, in deciding compassionate release motions. Those circuits reasoned that Congress explicitly made the sentencing changes non-retroactive and that § 3582(c)(1)(A) “should not provide a loophole to get around explicit non-retroactivity.”
For instance, the 3rd Circuit ruled, “We will not construe Congress’s nonretroactivity directive as simultaneously creating an extraordinary and compelling reason for early release.” The 7th held that “the discretionary authority conferred by § 3582(c)(1)(A)… cannot be used to effect a sentencing reduction at odds with Congress’s express determination embodied in… the First Step Act that the amendment to § 924(c)’s sentencing structure appl[ies] only prospectively.” The 8th said, “The compassionate release statute is not a freewheeling opportunity for resentencing based on prospective changes in sentencing policy or philosophy.”
The 3rd and 7th Circuits still allow district courts hearing compassionate release motions to consider First Step’s changes to stacked § 924(c) sentencing when analyzing § 3553(a) sentencing factors.
 The 1st, 4rth, and 10th Circuits, on the other hand, have all held that district courts may consider First Step’s non-retroactive changes to penalty provisions, in combination with other factors, when determining whether extraordinary and compelling reasons for compassionate release exist in a particular case. The Circuits have held that the statutes directly addressing “extraordinary and compelling reasons” don’t prohibit district courts from considering non-retroactive changes in sentencing law; and (2) a sentence reduction under § 3582(c)(1)(A)’s “extraordinary and compelling reasons” is “entirely different from automatic eligibility for resentencing as a result of a retroactive change in sentencing law.”
The 1st, 4rth, and 10th Circuits, on the other hand, have all held that district courts may consider First Step’s non-retroactive changes to penalty provisions, in combination with other factors, when determining whether extraordinary and compelling reasons for compassionate release exist in a particular case. The Circuits have held that the statutes directly addressing “extraordinary and compelling reasons” don’t prohibit district courts from considering non-retroactive changes in sentencing law; and (2) a sentence reduction under § 3582(c)(1)(A)’s “extraordinary and compelling reasons” is “entirely different from automatic eligibility for resentencing as a result of a retroactive change in sentencing law.”
The 6th Circuit swings both ways. In United States v. Jarvis, the Circuit held that the “district court, moreover, correctly concluded that it lacked the authority to reduce Jarvis’s sentence based on a nonretroactive change in the law.” But in United States v. Owens, the panel said that the disparity between a defendant’s actual sentence and the sentence that he would receive if the First Step Act applied can be considered, along with other factors, to be an extraordinary and compelling reason for a reduction.
In Howard’s case, the 9th said,
Congress has only placed two limitations directly on extraordinary and compelling reasons: the requirement that district courts are bound by the Sentencing Commission’s policy statement, which does not apply here, and the requirement that ‘rehabilitation alone’ is not extraordinary and compelling. Neither of these rules prohibits district courts from considering rehabilitation in combination with other factors. Indeed, Congress has never acted to wholly exclude the consideration of any one factor, but instead affords district courts the discretion to consider a combination of “any” factors particular to the case at hand… To hold that district courts cannot consider nonretroactive changes in sentencing law would be to create a categorical bar against a particular factor, which Congress itself has not done.
United States v. Chen, Case No 20-50333 (9th Cir., September 14, 2022)
Bloomberg, Compassionate Release Gets Another Look Under First Step Act (September 14, 2022)
– Thomas L. Root