We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

BOP COVID NUMBERS MAY BE CRESTING AS CRITICISM OF BOP PANDEMIC RESPONSE GROWS
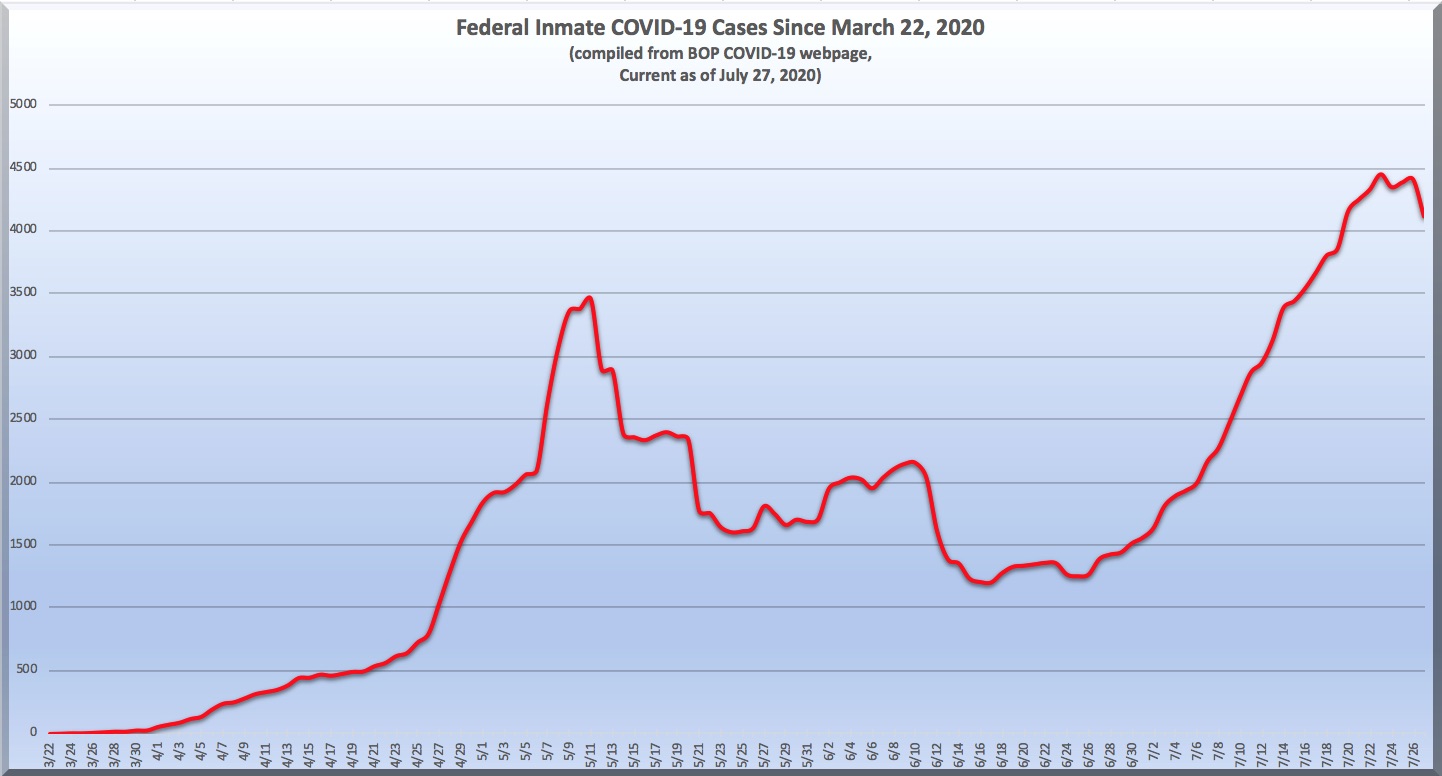
The number of Federal Bureau of Prisons prisoners with COVID-19 increased 14% last week to 4,413 as of Sunday night (an all-time high), after falling slight on Saturday. Yesterday, however, the number of infected inmates took a 7% plunge.
It appears that all of that decrease was due to FCC Beaumont’s dramatic (some might say ‘miraculous’) decrease in reported cases, from 463 on Sunday night to 135 on Monday night. But for that decrease, BOP systemwide cases increased by 35.
 Other numbers were not so encouraging. Infected BOP staff increased 33% to 405, and four more inmates died. Most ominously, 108 facilities have COVID-19, 88.5% of BOP joints, an increase of 9% over last week.
Other numbers were not so encouraging. Infected BOP staff increased 33% to 405, and four more inmates died. Most ominously, 108 facilities have COVID-19, 88.5% of BOP joints, an increase of 9% over last week.
Of the 4,120 active inmate cases, Texas facilities FCI Seagoville has 1,257, the women’s FMC at Carswell has 529 cases, and Beaumont Low has 463. Other significant outbreaks are at FCI Miami and Coleman Low and Medium (Florida), Victorville Medium I (California), Butner Low (North Carolina), Elkton (Ohio) and Jesup (Georgia).
A report from the Dept. of Justice Inspector General released last week criticized BOP mismanagement of the pandemic at Lompoc. The report said two Lompoc BOP staff members came to work in late March despite experiencing coronavirus symptoms, although those symptoms were not detected during screening. Officials then failed to test or isolate an inmate who reported that he had begun having symptoms two days earlier and later tested positive. And thus it started.
Medical staff shortage limited inmate and staff screening for COVID-19 symptoms, and other staff shortages resulted in Lompoc officials delaying for 15 days the full implementation of staff movement restrictions required by BOP for institutions with active COVID-19 cases.
What’s more, the BOP’s use of home confinement authority in April was “extremely limited.” As of May 13, the IG report said, over 900 Lompoc inmates had contracted COVID-19 but only 8 inmates had been transferred to CARES Act home confinement.
 In a statement following the release of the report, the BOP said it had fixed nearly all of the issues identified by the inspector general. It blamed the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines for many of the problems cited in the report. “These findings must be placed in context, as these were unique circumstances where the BOP, along with the rest of the country, was learning about how to treat and manage this novel virus,” the agency said.
In a statement following the release of the report, the BOP said it had fixed nearly all of the issues identified by the inspector general. It blamed the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines for many of the problems cited in the report. “These findings must be placed in context, as these were unique circumstances where the BOP, along with the rest of the country, was learning about how to treat and manage this novel virus,” the agency said.
Meanwhile, in Los Angeles Federal Court, Judge Consuelo Marshall granted a preliminary injunction in a class-action lawsuit brought by the American Civil Liberties Union of Southern California that accuses the BOP Lompoc management of failing to take basic hygiene steps to protect those imprisoned.
The Judge ordered BOP officials to tell the court which inmates are medically eligible under CDC risk guidelines for release as part of a plan to reduce the population.
 The BOP asked the judge to dismiss the lawsuit, noting it had built a field hospital and adopted mass testing in May. But after more than 70% of inmates at Lompoc Low tested positive, the judge found there was a “substantial risk of exposure to COVID-19, which is inconsistent with contemporary standards of human decency” and that the BOP had “likely been deliberately indifferent to the known urgency to consider inmates for home confinement, particularly those most vulnerable to severe illness or death.”
The BOP asked the judge to dismiss the lawsuit, noting it had built a field hospital and adopted mass testing in May. But after more than 70% of inmates at Lompoc Low tested positive, the judge found there was a “substantial risk of exposure to COVID-19, which is inconsistent with contemporary standards of human decency” and that the BOP had “likely been deliberately indifferent to the known urgency to consider inmates for home confinement, particularly those most vulnerable to severe illness or death.”
DOJ Inspector General, Pandemic Response Report 20-086, Remote Inspection of Federal Correctional Complex Lompoc (July 23, 2020)
CNN, DOJ watchdog report finds lack of staffing contributed to Covid outbreak in California prison (July 23)
Los Angeles Times, Judge orders release of vulnerable inmates at Lompoc prisons hit by virus (July 22)
Torres v. Milusnic, Case No 2:20cv4450 (C.D.Cal, entered July 14, 2020), 2020 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 131446
– Thomas L. Root