We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

EARNED TIME CREDITS – THE DEVIL’S IN THE DETAILS
 Probably the biggest selling point used by First Step Act supporters when Congress passed the measure in December 2018 was that the bill would deliver evidence-based programming to reduce recidivism. The inmates would be assessed under a new program that accurately gauged their likelihood to be recidivists and their needs that should be met to reduce that likelihood. The inmates would benefit, the public would benefit, the overcrowded and understaffed prisons would benefit, the U.S. Treasury would benefit. Everyone’s a winner!
Probably the biggest selling point used by First Step Act supporters when Congress passed the measure in December 2018 was that the bill would deliver evidence-based programming to reduce recidivism. The inmates would be assessed under a new program that accurately gauged their likelihood to be recidivists and their needs that should be met to reduce that likelihood. The inmates would benefit, the public would benefit, the overcrowded and understaffed prisons would benefit, the U.S. Treasury would benefit. Everyone’s a winner!
The programming to reduce recidivism, after more than a year of preparation, is supposed to begin in a week. But the devil’s in the details, and hope for a broad rollout that meets the expectations of First Step backers, let alone those of inmates, is dwindling rapidly.
 By now, virtually all inmates have undergone an initial assessment under PATTERN, the new risk and needs assessment program developed in response to the First Step Act. According to the Act (a provision now codified at 18 U.S.C. § 3621(h)(1)(B)), the Bureau of Prisons is to begin to expand the most effective evidence-based recidivism reduction programs and productive activities it currently offers and to add any new evidence-based recidivism reduction programs and productive activities necessary to effectively implement First Step by Jan. 20. Subsection (h)(2)(A) gives the BOP until Jan. 20, 2022, to provide such programming for all inmates. During the “phase in” period, priority placement in the programs is to go to people closest to their release date.
By now, virtually all inmates have undergone an initial assessment under PATTERN, the new risk and needs assessment program developed in response to the First Step Act. According to the Act (a provision now codified at 18 U.S.C. § 3621(h)(1)(B)), the Bureau of Prisons is to begin to expand the most effective evidence-based recidivism reduction programs and productive activities it currently offers and to add any new evidence-based recidivism reduction programs and productive activities necessary to effectively implement First Step by Jan. 20. Subsection (h)(2)(A) gives the BOP until Jan. 20, 2022, to provide such programming for all inmates. During the “phase in” period, priority placement in the programs is to go to people closest to their release date.
As an incentive for participating in the programs, the First Step Act provides eligible inmates with earned-time credits which can be used toward increasing pre-release custody (halfway house and/or home confinement) or swapping time inside the BOP for more supervised release. A Bloomberg Law article described it last week like this: “Earned time credits… do not reduce a prisoner’s sentence, per se, but rather allow eligible prisoners to serve their sentence outside prison walls.”
 But for a lot of reasons the question of whether the BOP is anywhere close to meeting the First Step Act’s timetable remains open. First, as the BOP admitted two weeks ago, PATTERN has not yet been adopted in its final form. Although the BOP has promised to identify its existing programs that will award inmates earned-time credits, it has not yet done so. What’s more, a surprising large number of federal inmates will not be eligible to receive earned time credits because the BOP has determined they are excluded by one or more of the 65 categories of crime or immigration statute exempted from the program by Congress.
But for a lot of reasons the question of whether the BOP is anywhere close to meeting the First Step Act’s timetable remains open. First, as the BOP admitted two weeks ago, PATTERN has not yet been adopted in its final form. Although the BOP has promised to identify its existing programs that will award inmates earned-time credits, it has not yet done so. What’s more, a surprising large number of federal inmates will not be eligible to receive earned time credits because the BOP has determined they are excluded by one or more of the 65 categories of crime or immigration statute exempted from the program by Congress.
The current limits on time in a halfway house (up to 12 months) and home confinement (the lesser of six months or 10% of the sentence) specified in 18 U.S.C. § 3624(c) will not apply to earned time credits. Thus, an inmate can be released to more than a year of halfway house or home confinement after accumulating earned time credits.
Bloomberg Law reported last week that any earned-time credits inmates receive for completing programs prior to the final implementation of the PATTERN tool – whenever that will be – will not be eligible for redemption until the tool is implemented. What’s more, the article reported, “the ability to start earning credits may not actually come for most prisoners until even later than that, depending on how long it takes the BOP to apply PATTERN and create programming and productive activities and assign prisoners to them.”
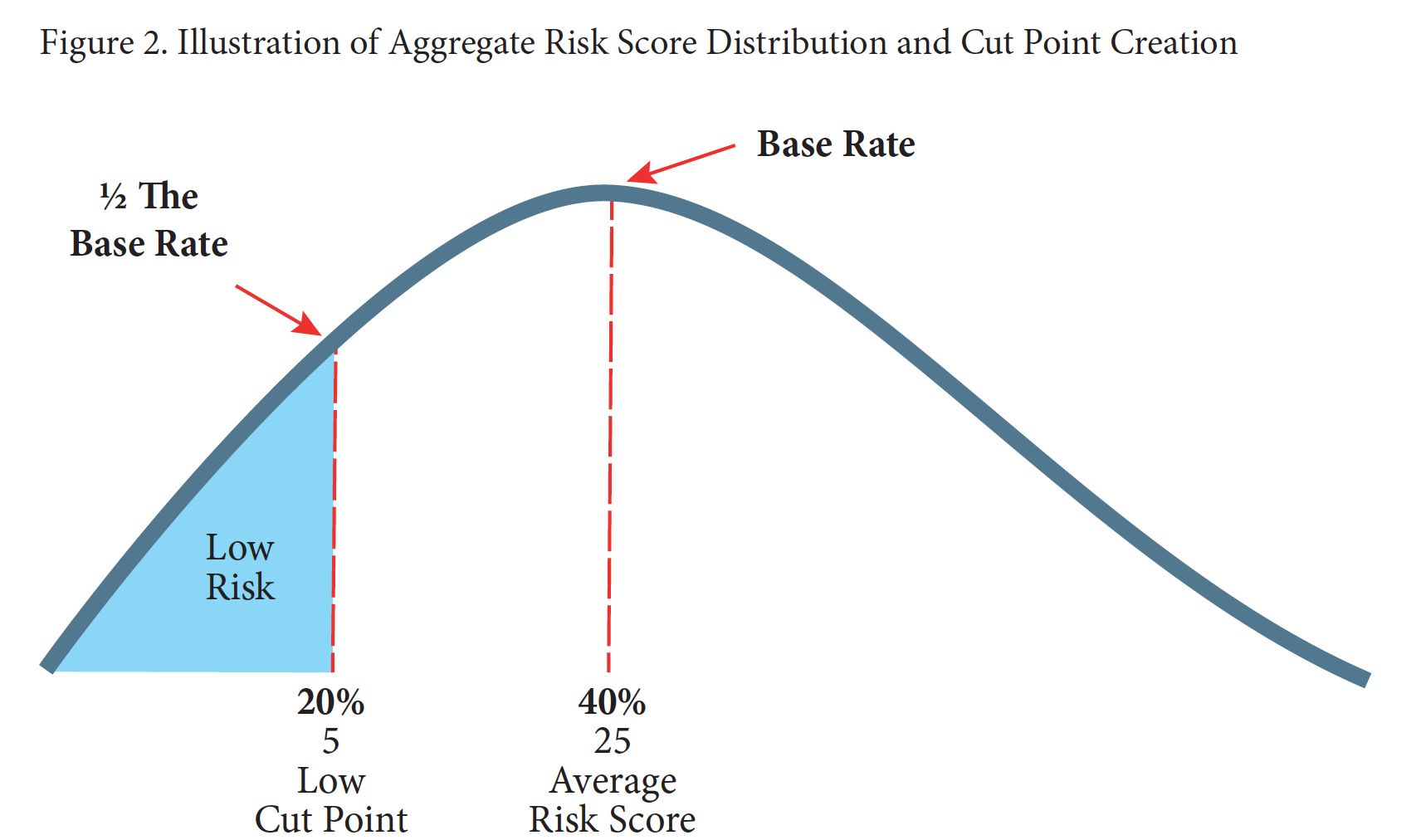
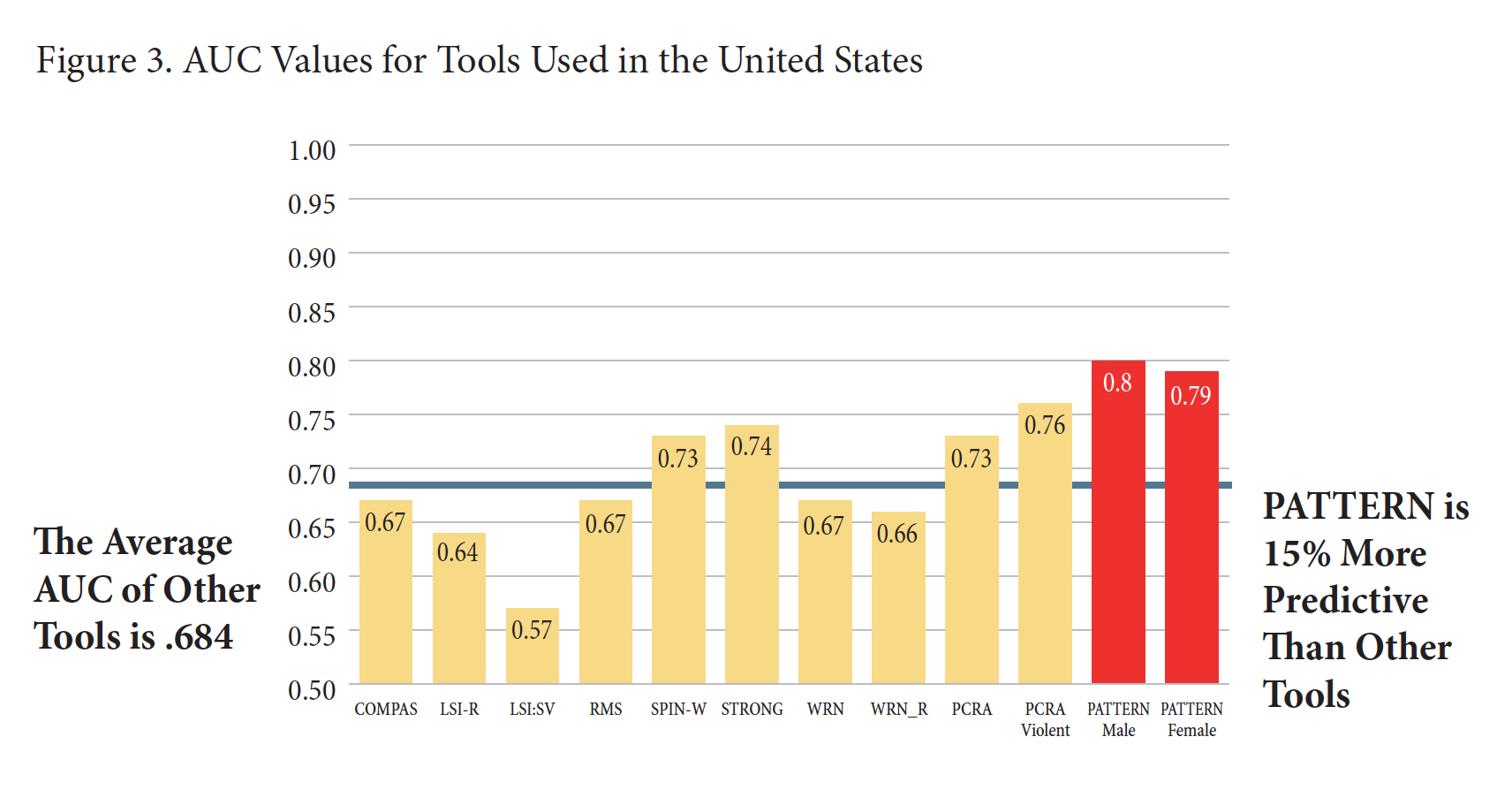
 PATTERN was the subject of a House Judiciary Committee Oversight hearing last October, where some experts expressed concern about its “racial bias and lack of transparency, fairness, and scientific validity.” The Dept. of Justice has not said how close PATTERN is to being finalized, stating only that it “is currently undergoing fine-tuning.” Indications are that inmates that have been scored so far have been analyzed under a preliminary version of the tool. Last July, DOJ estimates were that the final PATTERN program would be in place by Thanksgiving 2019.
PATTERN was the subject of a House Judiciary Committee Oversight hearing last October, where some experts expressed concern about its “racial bias and lack of transparency, fairness, and scientific validity.” The Dept. of Justice has not said how close PATTERN is to being finalized, stating only that it “is currently undergoing fine-tuning.” Indications are that inmates that have been scored so far have been analyzed under a preliminary version of the tool. Last July, DOJ estimates were that the final PATTERN program would be in place by Thanksgiving 2019.
A further impediment to full implementation of earned-time credit program will be the availability of halfway house beds. In most of the country, there is a shortage of available halfway house beds for federal inmates. The Act provides no additional funding or resources for the BOP to increase the loss of halfway house beds, which was at crisis levels several years ago.
“The BOP has a long history of acting in ways that result in lengthier and less productive terms of incarceration despite the obvious will of Congress,” David E. Patton, executive director of the nonprofit Federal Defenders of New York, was quoted as saying by the Washington Post. “For decades the BOP took an unreasonably restrictive view of good time, resulting in thousands of years of additional overall prison time. For decades it refused to exercise the authority given to it by Congress to release incarcerated people who were terminally ill, infirm, or otherwise suffered from extraordinary circumstances… and for decades it has not provided enough vocational, educational, mental health, and substance abuse programming despite abundant need and lengthy waitlists.” Pointing to DOJ data, Patton said wait lists include 25,000 prisoners for prison work assignments, 15,000 for vocational and educational training and 5,000 for drug treatment.
The Washington Post said last week that almost half of BOP prisoners complete no programs, more than half don’t get needed drug treatment, more than 80% haven’t taken technical or vocational courses, and more than 90% have no prison industry employment, according to data.
 “The BOP is struggling to fulfill the requirements of the Act as the Bureau is still more than 4,000 positions short,” Shane Fausey, president of the American Federation of Government Employees Council of Prison Locals, told the Post. He complained of “abusive overtime and mandatory double shifts,” adding that requirements of the First Step Act have worsened the crisis.
“The BOP is struggling to fulfill the requirements of the Act as the Bureau is still more than 4,000 positions short,” Shane Fausey, president of the American Federation of Government Employees Council of Prison Locals, told the Post. He complained of “abusive overtime and mandatory double shifts,” adding that requirements of the First Step Act have worsened the crisis.
BOP Director Kathleen Hawk Sawyer told the House oversight committee last October that the understaffing was over 3,700 vacancies and said resolving that “is among my highest priorities… but doing so will take time.”
Bloomberg Law, Insight: The First Step Act—Earned Time Credits on the Horizon (Jan. 9)
Washington Post, Federal prison reform has bipartisan support. But it’s moving slowly. (Jan. 9)
– Thomas L. Root