We post news and comment on federal criminal justice issues, focused primarily on trial and post-conviction matters, legislative initiatives, and sentencing issues.

LATE-BREAKING NEWS…
The Supreme Court granted certiorari in Jones v. Hendrix by order issued at 9:30 am on Monday, May 16.
Could the Justices be reading my blog? Doubtful, but the certiorari may be good news for thousands of federal inmates trapped in the 10th and 11th Circuits (depending, of course, on the outcome of this case sometime next year).
SCOTUS MAY FINALLY SETTLE THE 2241 DEBATE

Let’s say you were standing in front of Sunny’s Cigars with a gun and two prior convictions, one for selling drugs and the other for manslaughter. If the Feds picked you up, you would have been sentenced to a minimum 15 years under 18 U.S.C. § 924(e), the Armed Career Criminal Act.
After the U.S. Supreme Court (generally known by the shorthand “SCOTUS“) ruled in Borden v. United States that a crime committed through recklessness was not a “crime of violence” predicate for ACCA, you would want to file with your sentencing court to get the ACCA sentencing enhancement thrown out.
The Borden ruling was not a constitutional ruling, but instead just an interpretation of a statute. That meant that you could not file a second-or-successive 28 U.S.C. § 2255 motion, because 28 U.S.C. § 2244(b) limits successive § 2255s to newly discovered evidence or decisions on constitutionality. However, 28 U.S.C. § 2255(e) – known as the “saving clause,” lets you file a traditional 28 U.S.C. § 2241 habeas corpus motion attacking the ACCA sentence where a § 2255 would be inadequate to address the issue.
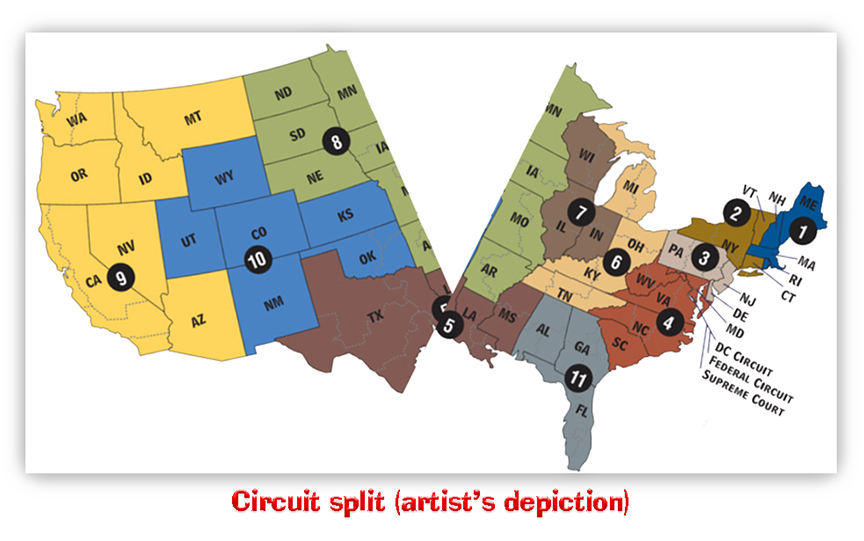
Or at least it would let you file a § 2241 petition if you’re locked up in, say, Kentucky (in the 6th Circuit). A § 2241 habeas corpus petition is filed in the federal district in which you’re located at the time you file. If you were at FCI Manchester, you’d file in the Eastern District of Kentucky. Go a few miles east of there to do your time in Beckley, West Virginia, for example, and you’d be filing in the Southern District of West Virginia (4th Circuit). Fourth Circuit precedent forecloses you from using a § 2241 petition as a workaround.
 Writing in SCOTUSBlog last week, John Elwood noted that Ham v. Breckon, a 4th Circuit decision, and Jones v. Hendrix, an 8th Circuit decision, both asked the same question, and both have been “relisted” by the Supreme Court.
Writing in SCOTUSBlog last week, John Elwood noted that Ham v. Breckon, a 4th Circuit decision, and Jones v. Hendrix, an 8th Circuit decision, both asked the same question, and both have been “relisted” by the Supreme Court.
A “relist” is a petition for certiorari that is scheduled to be decided at the Supreme Court’s regular Friday conference, but is “relisted” to be considered further at a subsequent conference. A “relisted” petition is statistically more likely to have review granted by the Court, and that is even more likely where there are two relisted petitions asking the same question.
This is important, because two circuits – the 10th and 11th – don’t permit § 2241 petitions even where the movant is challenging guilt or innocence. A SCOTUS decision on Ham or Jones would not only settle whether a movant could challenge a statutory sentencing enhancement using a § 2241 petition under the “saving clause,” but would address the circuit split between the two outlier circuits (the 10th and 11th) and everyone else on whether guilt and innocence could be challenged as well.
 Elwood thinks that, while the Court has ducked the issue in the past, it will grant review this time. He wrote, “The government — which generally is a pretty successful respondent as well as a successful petitioner — admits that there is a circuit split on the issue. It would have a hard time saying otherwise, since the government itself petitioned for Supreme Court review on this very issue a couple years back in the much-relisted United States v. Wheeler, before a vehicle problem arose (the prisoner… was released from prison) that apparently persuaded the Supreme Court to deny review in that case.”
Elwood thinks that, while the Court has ducked the issue in the past, it will grant review this time. He wrote, “The government — which generally is a pretty successful respondent as well as a successful petitioner — admits that there is a circuit split on the issue. It would have a hard time saying otherwise, since the government itself petitioned for Supreme Court review on this very issue a couple years back in the much-relisted United States v. Wheeler, before a vehicle problem arose (the prisoner… was released from prison) that apparently persuaded the Supreme Court to deny review in that case.”
Ham v. Breckon, Case No 21-763 (pending certiorari)
Jones v. Hendrix, Case No 21-857 (certiorari granted)
SCOTUSBlog, Challenges to administrative action and retroactive relief for prisoners (May 11, 2022)
– Thomas L. Root

